Excretion
Excretion is defined as the removal of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism, and substances in excess of requirements in the body.
For example:
- Kidneys excrete urea and excess water and salts to form urine
- Lungs excrete carbon dioxide
Urea is the waste product formed in the liver, urine is made in the kidneys and is the combination of urea with water and other salts
Urea is formed by deamination. Deamination is the removal of the nitrogen containing part of excess amino acids to form urea.
Urinary system
Production and removal of urine
The urinary system is composed of the kidneys, ureter, the bladder, and the urethra.

- Urea is made in the liver, and enters the kidneys.
- Urea, water and other substances make urine
- Urine is passed onto the bladder to be stored (via the ureter)
- The urine is eventually excreted from the body through the urethra
Volume and concentration of urine
The volume and concentration of urine may depend on certain factors:
- Hydration
- More water intake leads to more excess water. This means the volume of urine will increase and the concentration will decrease
- Hot-temperatures (dehydration)
- Dehydration results in less excess water. This means the volume of urine will decrease and the concentration will increase
Kidney
Structure of the kidney
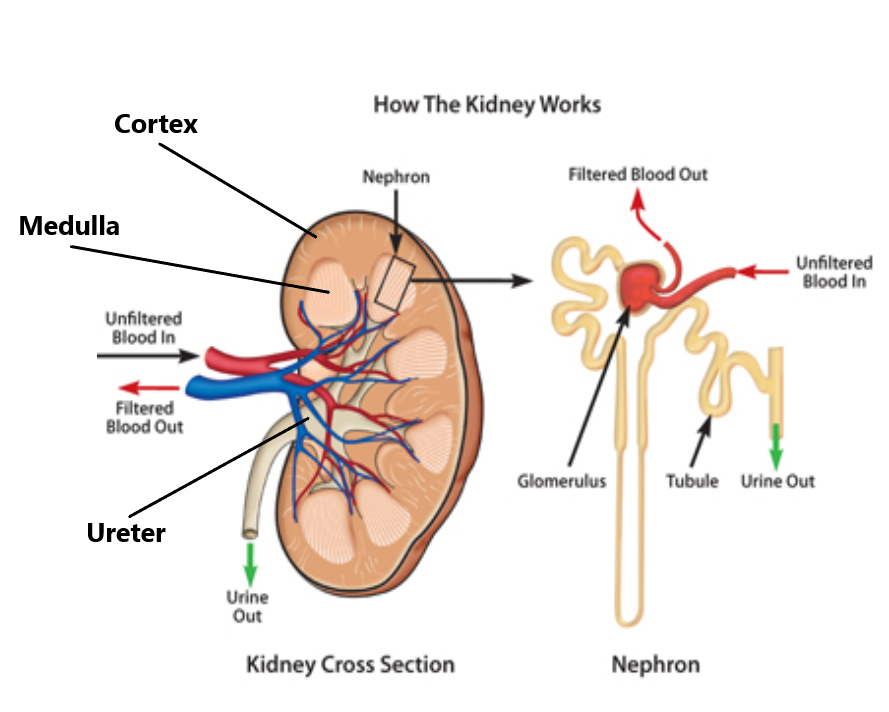
Kidney tubules (nephrons)
The medulla of the kidneys are made of kidney tubules called nephrons.
The glomerulus (beginning of the tubule) filters water, glucose, urea and salts from the blood. The rest of the tubule reabsorbs most (but not all) of the glucose, water and salts back. The urea remains in the tubule.
The urea along with the other remaining components in the tubule is what we call urine. The urine leaves the kidney via the ureter and eventually leaves the body through the urethra.
Kidney machines
As detailed above, the kidneys play a major role is removing the urea from our blood.
If a patient has kidney dysfunction, then other methods must be used to remove the urea instead.
Kidney dialysis
Kidney dialysis is the method of removingurea from the blood via diffusion.

The blood is extracted and made to pass through tubes in the dialysis machine (see diagram above).
The tubes have a semi-permeable membrane, and the fluid outside of the tube is called the bathing liquid.
The bathing liquid is made to have a similar concentration of substances as the blood except urea.
The low urea concentrations in the bathing liquid means that urea will diffuse out of the blood as it passes through the tube in the machine.
Other important substances such as glucose, proteins, etc. will remain in the blood because there is no concentration gradient between the bathing fluid & the blood.
Kidney transplant
The main advantage of a kidney transplant as opposed to kidney machines is that they can return to a normalized lifestyle (i.e. no need for regular visits to use the machine). Moreover, it would save the cost of using the kidney machines themselves.
However, for a kidney transplant to work a suitable donor is required which may often be difficult to find. Moreover, there is always the chance of a tissue rejection.