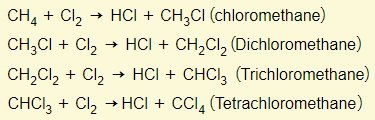Properties of alkanes
Alkanes have the general formula:
![]()
They are hydrocarbons (compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen) that only have single bonds. Since no more atoms can add onto the molecule they are described as saturated hydrocarbons. They are generally unreactive except for combustion and chlorination (substitution reaction).
Note: The combustion and substitution reactions of alkanes will be covered down below
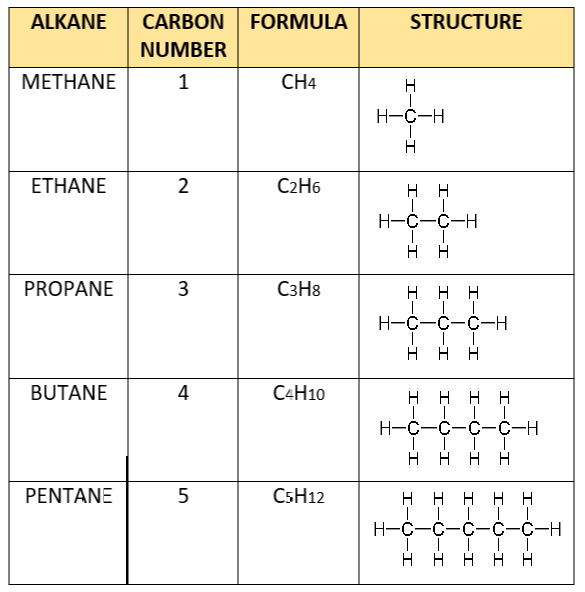
Alkane homologous series
Alkane reactions
Combustion
The complete combustion of an alkane gives carbon dioxide and water
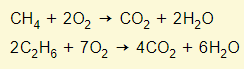
The incomplete combustion of an alkane gives carbon monoxide and water
![]()
Substitution
Alkanes react with chlorine in bright light to give a mixture of chloroalkanes. One hydrogen atom is substituted by one chlorine atom.
Provided that there is enough chlorine present, the reaction can continue until all hydrogen atoms in the compound have been substituted.
Lets take methane as an example: