Air
Composition of air
The composition of clean, dry air is approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and the remaining 1% is a mixture of noble gases and carbon dioxide.
Nitrogen and oxygen can be separated from air by liquefying air first and then separating the two gases via fractional distillation.
- Air liquefaction
- Air is first filtered to remove dust
- Cooled to -200 degrees to make gas air into liquid
- Fractional distillation (of liquid air)
- Liquid air passed into bottom of fractionating column
- Column warmer at the bottom than the top
- Liquid nitrogen boils at the bottom of the column
- Gaseous nitrogen rises to the top where it is piped off at stored
- Liquid oxygen collects at the bottom of the column
Pollutants
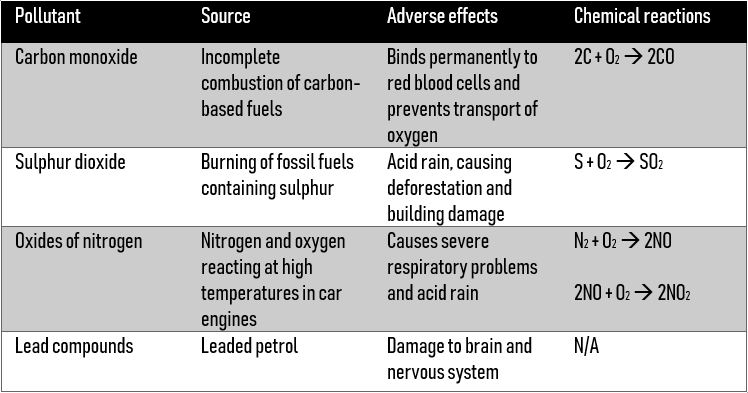
Oxides of nitrogen and carbon monoxide are pollutants produced by motor vehicles. Catalytic converts can reduce pollution by catalyzing the reactions below:
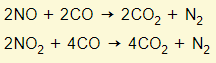
Nitrogen and carbon dioxide are fairly harmless, and these gases leave the car exhaust.
Rust
Rusting is the red/orange coating that forms on the surface of iron when exposed to air and moisture.
The term rusting is specific to iron or steel. Every other metal will corrode.
Rusting is essentially a redox reaction whereby iron reacts with the air and water to form hydrated iron (III) oxide. Therefore both oxygen and water must be present for rusting to occur.
Most methods of rust prevention involve coating the iron or steel in order to prevent contact with water and oxygen:
- Painting – For example, cars, ships, bridges etc.
- Using oil or grease – Effective for moving parts of machinery to be used as a lubricant and a protective coating
- Coating with plastic – Such as freezers, garden furniture etc.
- Planting – Cans of food are plated with tin
- Galvanising This is coating with zinc and has the great advantage of sacrificial protection (more info below)
When the zinc coating of galvanized steel falls apart, the steel will still not rust due to sacrificial protection. This is because the more reactive metal zinc (as shown in the reactivity series) will form ions more readily than iron. Under normal circumstances, the iron would oxidize (i.e. lose electrons) and become iron (III) cations which forms hydrated iron (III) oxide – which is rust. However if the steel is galvanized, then zinc will form zinc ions instead of iron therefore preventing the formation of rust.
Nitrogen and fertilizers
Fertilizers
Plants need the three elements nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium for healthy growth. These are removed from the soil when plants are harvested. The essential plant nutrients are replaced by NPK fertilizers. A typical NPK fertilizer might containing ammonium nitrate, ammonium phosphate, and potassium chloride.
Displacement of ammonia from its salts
The weak base, ammonia, is displaced from its salt by stronger bases. For example:
![]()
Haber process
Ammonia is manufactured from nitrogen and hydrogen. Please note that the forward reaction is exothermic.
![]()
Nitrogen is obtained from the air. Hydrogen is made from methane (natural gas).
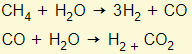
The conditions for the haber process are as follows:
- 450 degrees Celsius
- 200 atmospheres
- Iron catalyst
CIE likes to ask about why temperatures above 450 degrees is not used. This is because the forward reaction is exothermic and higher temperatures will favor the reverse reaction and therefore reducing yield. Too low temperatures on the other hand, will also lower reaction rates too. 450 degrees celsius is a good mid point.
Carbon dioxide and methane
Sources of carbon dioxide & methane
There are three main methods by which carbon dioxide is formed:
- By complete combustion of carbon-based fuel
- In respiration, which occurs in cells and plants of animals and provides energy for all living processes
- By reaction of carbonates with acids to form a salt, carbon dioxide and water
- Reaction between acids and carbonates
- Thermal decomposition of a carbonate
The main source of methane is as follows:
- Decomposition of vegetation and waste gases from digestion in animals
Global warming
Carbon dioxide and methane are greenhouse gases. This means that these gases trap heat in the atmosphere in order to keep the earth warm.
However as emissions of carbon dioxide and methane increases due to human activity, an excessive amount of heat becomes trapped in the atmosphere. This leads to excessive increase in the earth’s temperature, resulting global warming.
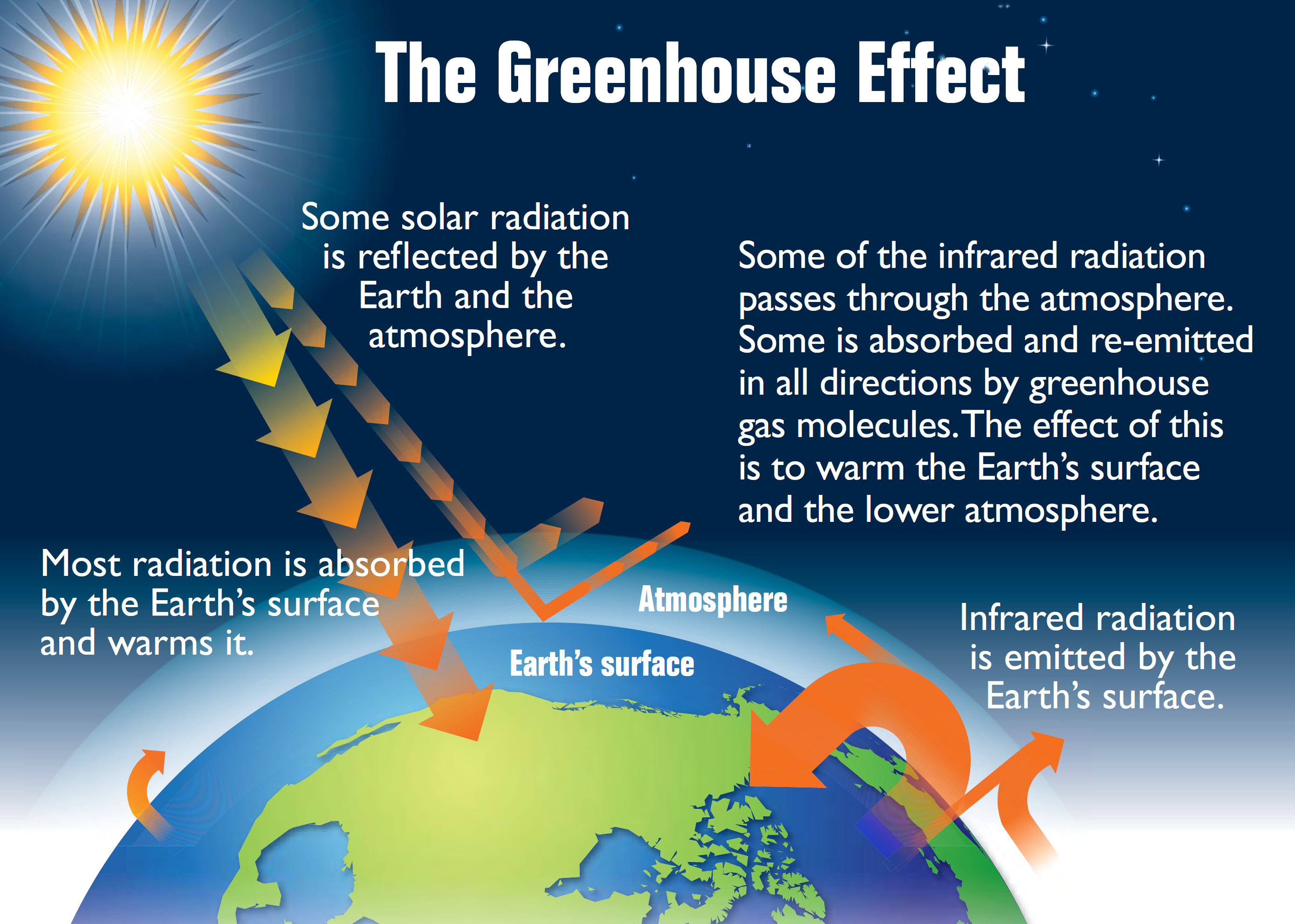
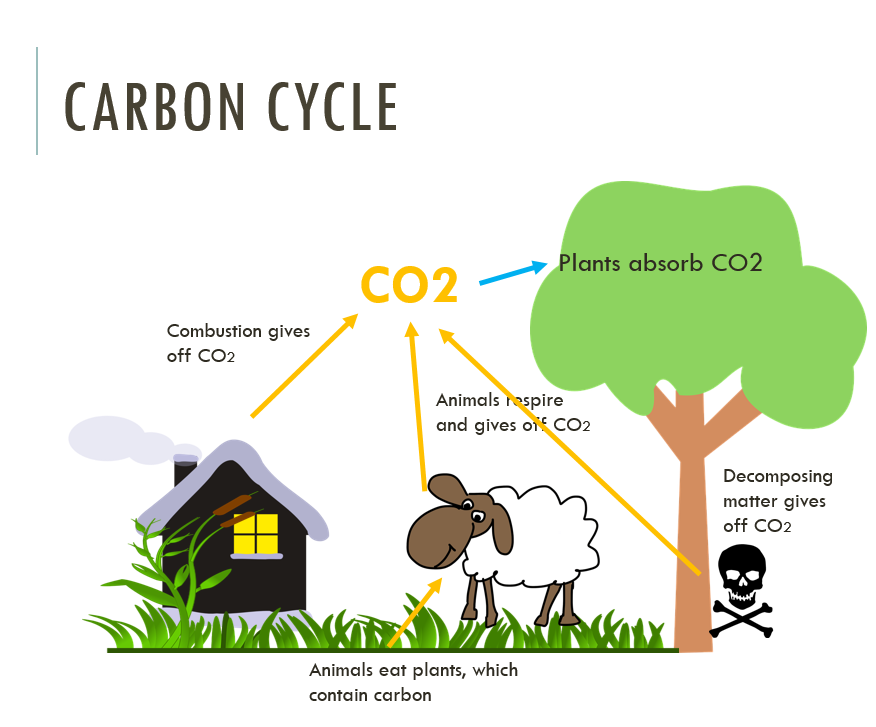
Carbon cycle
You are required to know the basic carbon cycle. This diagram below demonstrates this quite well.
Water
Chemical tests for water
Water will turn anhydrous copper (II) Sulfate from white to blue
![]()
Water will turn anhydrous cobalt chloride from blue to pink. This test can be carried out using cobalt chloride paper
![]()
Both tests indicate only the presence or absence of water. It does not provide information about the purity of water.
Treatment of water supply
Here are some brief points discussing how water is treated:
- Filtration (through sand and gravel filters) to remove undissolved solids
- Treated with chlorine to kill bacteria
- Supplied to the consumer – Safe to drink
Implications of inadequate supply of water
Poor water supply impacts health by causing acute infectious diarrhea, repeat or chronic diarrhea episodes, and non-diarrhoeal disease, which can arise from chemical species such as arsenic and fluoride. It can also affect health by limiting productivity and the maintenance of personal hygiene.
Also the lack of water supply will affect crops which need to be irrigated with water. This may in turn reduce the food supply due to reduced crop yields.